Elite Body Fat Percentages
Let's break down the national body fat percentages among athletes and what options exist for body composition tests.
Elite athletes typically maintain lower body fat percentages and minimal visceral fat through rigorous training, disciplined nutrition, and optimal lifestyle choices. However, body composition can vary based on the sport, position, and individual factors.
The body fat percentages for athletes in the top 5% of endurance sports—such as long-distance running, cycling, swimming, and triathlon—are typically very low due to the high volume of aerobic training. These athletes aim for lean physiques that optimize oxygen efficiency, speed, and endurance. However, body fat levels can vary slightly by age due to metabolic changes, recovery needs, and hormonal shifts. Below are typical body fat percentage ranges for elite endurance athletes in the top 5%:
Body Fat Percentage: Represents the proportion of fat mass to total body mass.
Visceral Fat Percentage: Refers to the fat stored around internal organs.
General Ranges for Elite Athletes
The following ranges are approximate and can vary based on the sport (e.g., endurance vs. power sports), position, and individual physiology.
Men: Body Fat Percentage Chart
Age Group | Elite Athletes | Amateur Athletes |
20s | 6-10% | 10-18% |
30s | 7-11% | 12-20% |
40s | 8-12% | 15-23% |
50s | 10-14% | 18-25% |
60s | 11-16% | 20-28% |
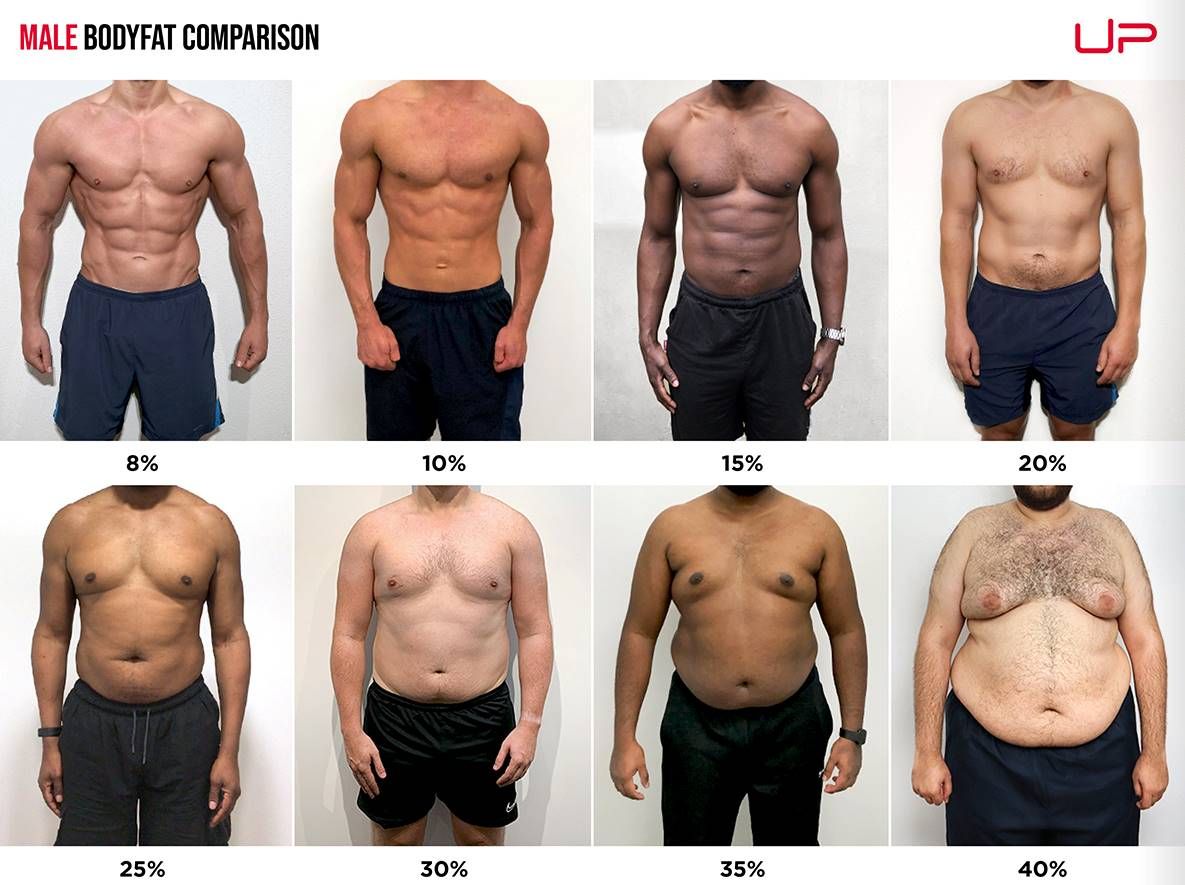
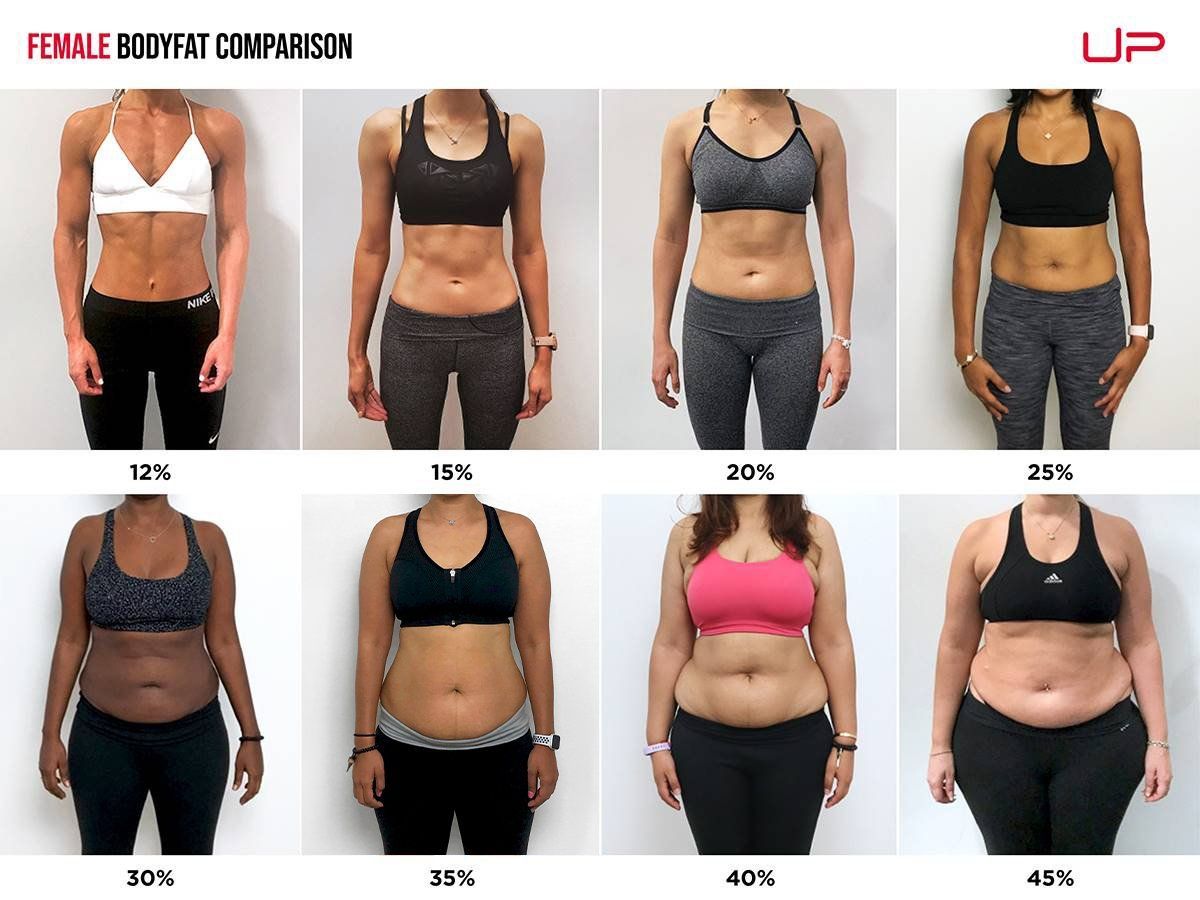
Women: Body Fat Percentage Chart
Age Group | Elite Athletes | Amateur Athletes |
20s | 10-15% | 12-18% |
30s | 11-17% | 14-20% |
40s | 12-19% | 16-25% |
50s | 14-22% | 19-27% |
60s | 16-25% | 23-30% |

source: Ultimate Performance
Important notes:
Men generally have lower body fat percentages than women due to physiological differences in fat distribution.
Younger athletes can maintain lower body fat levels due to faster metabolism and recovery capacity.
Women require higher essential fat for hormonal balance and reproductive health, even at elite levels.
Older athletes in their 40s, 50s, 60s, and 70s tend to have slightly higher body fat due to reduced metabolism and increased recovery time, though the best performers still maintain relatively low percentages.
Key Factors Influencing Elite Athlete Body Composition
Sport-Specific Demands:
- Endurance Sports: Favor lower body fat for enhanced performance and efficiency.
- Strength/Power Sports: Require higher muscle mass and may accommodate slightly higher body fat percentages for strength and power output.
Training Regimen:
- Aerobic Training: Helps reduce body fat and maintain low visceral fat levels.
- Resistance Training: Preserves and builds lean muscle mass, which can aid in maintaining a lower overall body fat percentage.
Nutrition:
- Caloric Balance: Maintaining an optimal balance between calorie intake and expenditure is crucial for low body fat.
- Macronutrient Composition: High protein intake supports muscle maintenance, while balanced carbohydrates and healthy fats support energy needs and metabolic health.
Recovery and Lifestyle:
- Adequate Sleep: Essential for hormonal balance and muscle recovery.
- Stress Management: Helps prevent cortisol-induced fat accumulation, particularly visceral fat.
Challenges with Aging
Metabolic Slowdown: As athletes age, their metabolism naturally slows, making it more challenging to maintain low body fat percentages.
Hormonal Changes: Declines in hormones like testosterone (men) and estrogen (women) can affect body composition and fat distribution.
Injury and Recovery: Older athletes may face longer recovery times, necessitating adjustments in training intensity and volume to prevent fat gain and muscle loss.
Body Composition Tests now more widely available
There are many different types of tools and techniques to measure body composition. Here are the two that we believe check off the most boxes when factoring in affordability, accuracy, ease of use and accessibility.
DEXA Scan (Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry)
A DEXA Scan uses low-level X-ray beams to measure body composition, including bone density, fat mass, and lean muscle mass. The machine emits two X-ray beams at different energy levels, which pass through the body and are absorbed by various tissues at different rates. Bone absorbs more X-rays, while fat and lean tissues absorb less. The scan is performed with the person lying flat on a table while the X-ray arm moves over the body, taking detailed measurements. This provides highly accurate data on body fat distribution, including visceral fat (fat around internal organs), and distinguishes between subcutaneous fat and lean muscle tissue. DEXA is considered one of the most precise methods for body composition analysis, commonly used in clinical settings to assess overall health, bone health, and obesity-related risks.
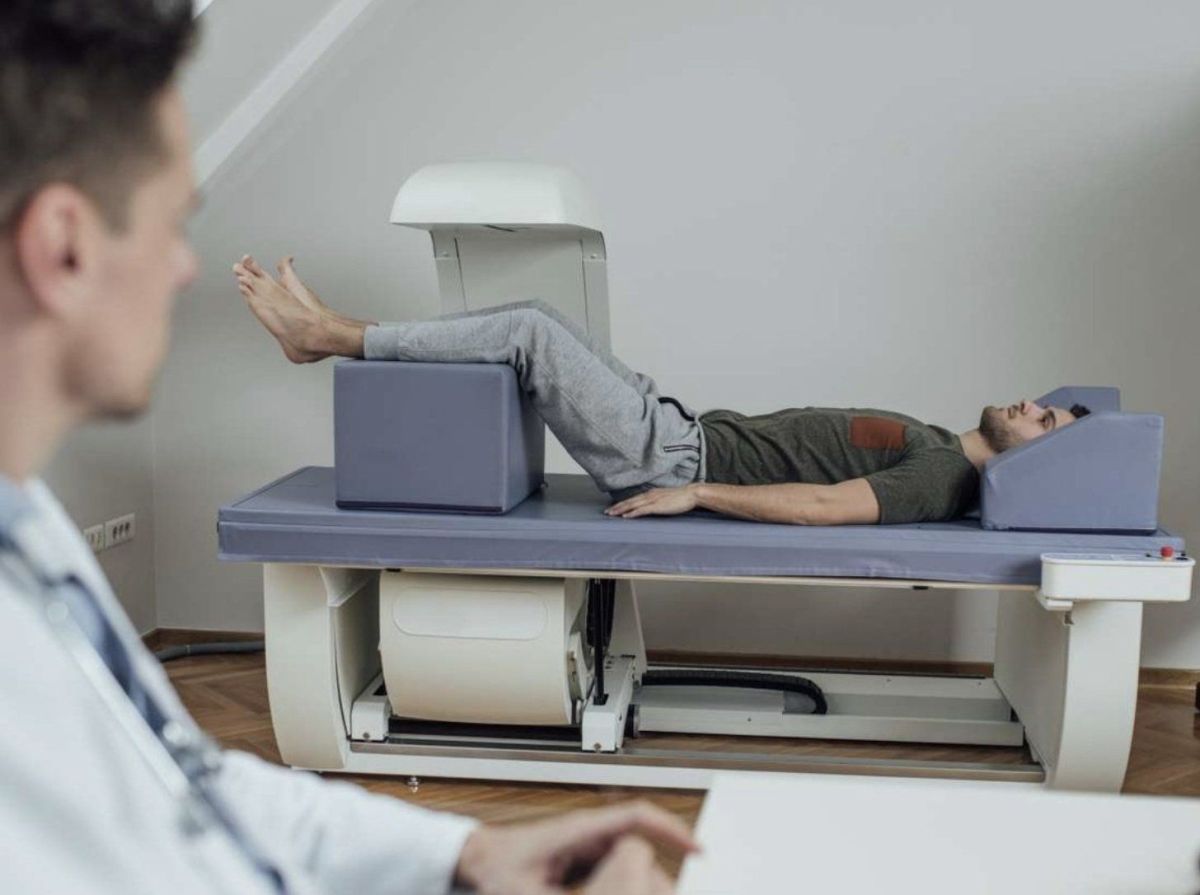
When used for body composition, DEXA Scan can be used by anyone, without the need for a prescription. The process is fast (<15 min) and painless while laying down. Fitness enthusiasts, athletes, and dieters often use body composition scans to get a baseline of where they are now to objectively measure their progress. Out of pocket costs for this test ranges from $150 - 300.
Find a nearby DEXA scan location site.
3D Body Composition Scans
A 3D Body Composition Scan uses cameras or infrared sensors to capture a 360-degree image of the body's surface. The individual stands on a rotating platform, while cameras or scanners take multiple images from various angles. These images are stitched together to create a 3D model of the body. From this model, software calculates estimates of body fat percentage, lean muscle mass, and other metrics based on body shape and volume. Unlike DEXA, it doesn't directly measure fat or muscle; instead, it uses algorithms to estimate composition based on size and proportions. This method is quick, non-invasive, and ideal for tracking changes over time, but it's less accurate for determining visceral fat compared to DEXA.
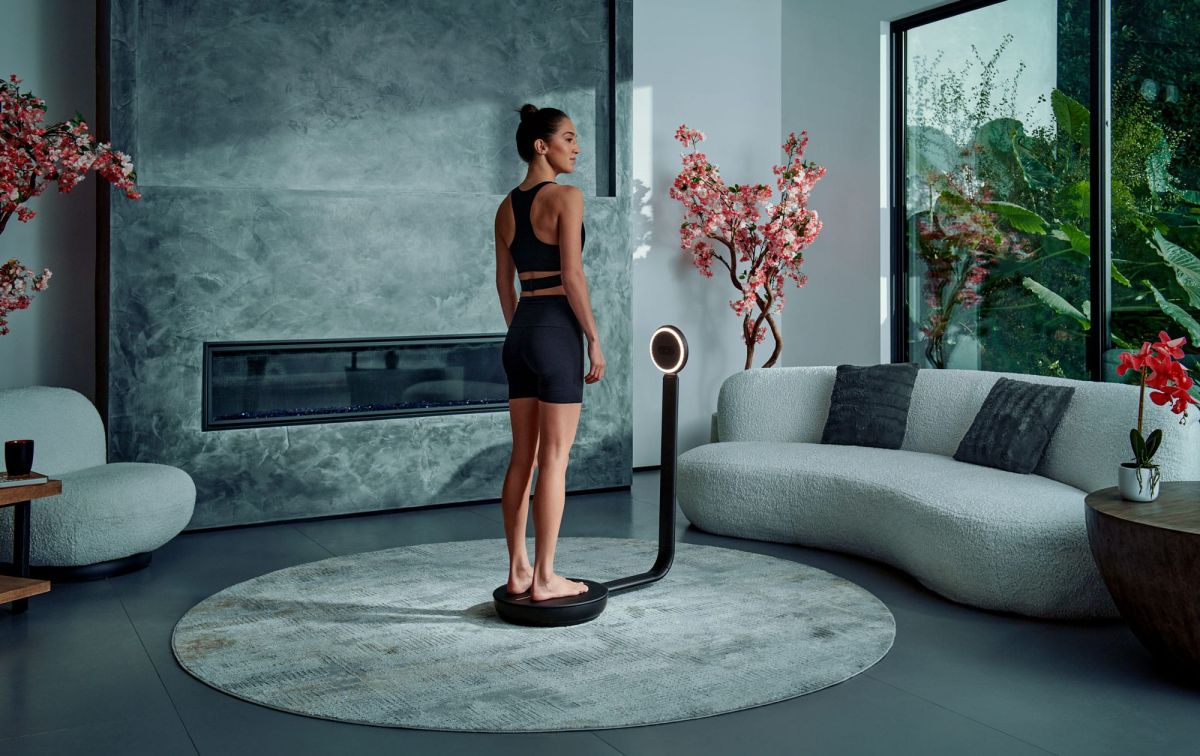

source: shapescale.com
Both tests offer useful insights but serve different purposes depending on the level of accuracy required. Two leading 3D Body Composition scanners include Styku and ShapeScale. The degree of accuracy for these machines for body composition read outs is +/- 3-4%. Meaning, if a DEXA scan reported 20% body fat, the Styku or ShapeScale may show 19-21%. So they are fairly accurate for your first test, and then even more accurate if you take future tests under the same conditions to do trend analysis.